When considering the differences between smallpox and chickenpox, it’s essential to understand the unique characteristics of each disease. You may be wondering what sets smallpox vs chickenpox apart, and what are the key facts to know about these two distinct illnesses. The differences between smallpox and chickenpox are crucial in determining the best course of treatment and prevention methods.
Smallpox, which was eradicated in 1980, had a significantly higher fatality rate compared to chickenpox, with approximately 30% of historical cases being fatal. In contrast, chickenpox is still a common illness, especially among children, with up to 90% infection rate among people not immune to the disease when exposed. Understanding the smallpox key facts and the distinctions between smallpox and chickenpox can help you make informed decisions about your health.
By recognizing the differences between smallpox and chickenpox, you can better navigate the world of pox diseases and take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. The annual prevention of approximately 3.5 million chickenpox cases through vaccination in the US is a testament to the importance of immunization efforts in controlling and eliminating these diseases. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the world of smallpox and chickenpox, exploring the historical context, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for each disease.
Understanding the Basics of Pox Diseases
When considering a chickenpox comparison, it’s essential to understand the pox disease distinctions and how smallpox and chickenpox are explained in the context of their causes and symptoms. You should know that smallpox was caused by the variola virus, while chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This distinction is crucial in understanding the historical context and current status of these diseases.
In the United States, routine smallpox vaccinations ceased in 1972, and the last smallpox outbreak was in 1949. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a smallpox vaccine booster every three years for those needing it due to their job. It’s worth noting that smallpox vaccination is believed to provide protection for decades, and the vaccine leaves a scar due to the use of live, unaltered virus (vaccinia).
- Smallpox was eradicated in 1980 by the World Health Assembly.
- About 30% of smallpox cases resulted in death.
- Before the chickenpox vaccine, there were about 4 million cases a year.
- Up to 90% of those close to a person infected with chickenpox may become infected.
Understanding the basics of pox diseases, including the chickenpox comparison and pox disease distinctions, is vital for making informed decisions about your health. By knowing the differences between smallpox and chickenpox, you can better protect yourself and your loved ones from these diseases.
| Disease | Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
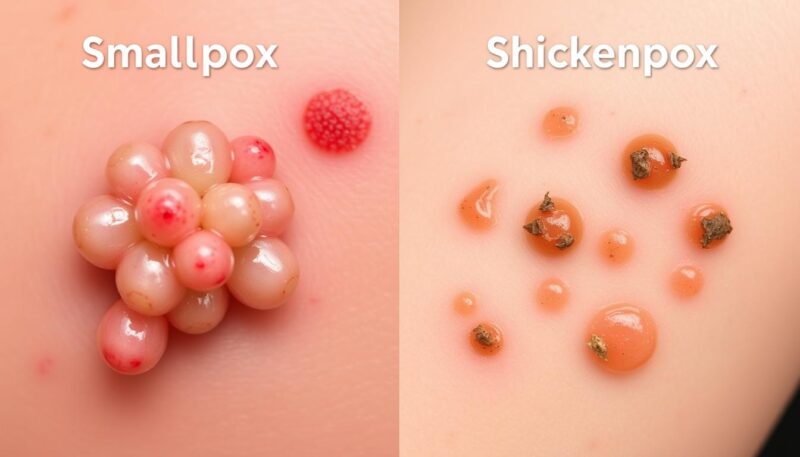
| Smallpox | Variola virus | Fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic rash |
| Chickenpox | Varicella-zoster virus | Fever, headache, and a blister-like rash |
Key Difference Between Smallpox and Chickenpox
When considering smallpox vs chickenpox, it’s essential to understand the differences between these two viral infections. Smallpox, caused by the variola virus, was a severe disease with a high mortality rate, killing over 300 million people in the 20th century. In contrast, chickenpox, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, is generally a mild illness, but it can lead to complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
The differences between smallpox and chickenpox are significant, with distinct symptoms, transmission, and treatment options. Chickenpox is characterized by a fever and rash, and most people recover within 1 to 2 weeks. The varicella vaccine has made chickenpox much rarer in the United States, with a 98% effectiveness rate. On the other hand, smallpox has not been reported in the U.S. for over 65 years due to the vaccine.

Understanding the viral infection differences between smallpox and chickenpox is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. The following are key differences:
- Smallpox has a higher mortality rate, with 3 out of 10 infected individuals succumbing to the disease.
- Chickenpox is generally a mild illness, but it can lead to complications, such as pneumonia and encephalitis, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- The varicella vaccine is up to 98% effective in preventing chickenpox, while the smallpox vaccine is not routinely given, except to individuals working with similar viruses or the military.
In conclusion, the differences between smallpox and chickenpox are significant, and understanding these differences is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the distinct symptoms, transmission, and treatment options for each viral infection, you can better manage your health and reduce the risk of complications.
Symptoms and Treatment Approaches
When it comes to smallpox key facts and chickenpox comparison, understanding the symptoms and treatment approaches is crucial. You should be aware of the pox disease distinctions to provide proper care and attention. Smallpox and chickenpox are two distinct diseases with different symptoms and treatment methods.
Smallpox symptoms include a high fever, headache, and a characteristic rash, while chickenpox symptoms include a fever, headache, and a blister-like rash. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary, and it’s essential to seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time.
Smallpox Symptoms and Treatment Methods
Smallpox treatment is primarily focused on supportive care, as antiviral treatments are limited. This includes managing symptoms and preventing complications such as pneumonia and encephalitis. Experimental treatments, including antiviral drugs and immune-based therapies, have been investigated.
Chickenpox Symptoms and Treatment Options
Chickenpox treatment options include symptomatic relief measures such as antihistamines, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and calamine lotion. Vaccination soon after exposure to chickenpox can prevent or reduce the severity of the disease. The varicella vaccine is widely recommended as part of childhood immunization programs in many countries.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical care are essential for controlling severe instances or complications that may arise from chickenpox. Preventive measures, including vaccination, post-exposure prophylaxis, and proper hygiene practices, are crucial in minimizing the spread of chickenpox within communities. By understanding the symptoms and treatment approaches for smallpox and chickenpox, you can provide better care and attention to those affected by these diseases.
Conclusion: Understanding the Distinction for Better Health Management
As you’ve learned, the differences between smallpox and chickenpox are crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and successful prevention strategies. While smallpox was eradicated globally in 1980 thanks to widespread vaccination efforts, chickenpox remains a common childhood illness that can be largely controlled through immunization programs.
Recognizing the unique symptoms, transmission patterns, and public health implications of these viral infections is essential for healthcare providers and individuals alike. Early and precise identification of smallpox is vital due to its highly contagious nature, requiring strict quarantine and infection control measures. In contrast, chickenpox diagnosis is primarily clinical, with antiviral medications and supportive care playing a key role in management.
By understanding the distinctions between these viral infections, you can make informed health decisions, seek appropriate medical attention, and contribute to the overall well-being of your community. Staying up-to-date on vaccination recommendations and practicing good hygiene habits can go a long way in preventing the spread of these diseases and safeguarding your health.